
Morse Code
In the computer science world, Morse Code is one of those old-timey technologies that’s still cool. We’ve all watched movies about WWII where governments send telegraphs using Morse Code to transmit messages across huge distances. We’ve probably also watched Navy movies where ship commanders are sending the famous “SOS” when a ship is in trouble. This technology was ground-breaking when it was developed, and it’s still relevant today.
Since I was interested in this, I thought it would be cool to create Morse Code with a program if I could. I Googled this for a little while, and found several people used the Web Audio API to generate Morse Code with Javascript. Then I spent subsequent time reading (and coding) with both Javascript Timers and the Web Audio API playing with different methods of sending messages via light (colors) and sound.
And ultimately, since a lot of this was kinda cool, I decided to write a post on it.
The rest of this post is going to cover some cool ways to create Morse Code with Javascript. I’m going to walkthrough implementations using both the Web Audio API and Javascript’s setTimeout function.
Some History about Morse Code
Morse Code (pronounced like the “Morse” in “Morsel”, not “Morris” like the name, as my wife described to me) can be defined as an encoded language of “dots” and “dashes” that correspond to a preset table of characters. The characters include the alphabet (a-z) as well as numbers (0-9) and some punctuation. The “dots” and “dashes” that compose Morse Code can be transmitted via anything that can produce a varied signal. That makes it really powerful because as long as both the sender and receiver understand Morse Code, messages can be sent across long distances with a flashlight or radio. With the invention of the telegraph, this became even more powerful as messages could be transmitted over very long distances as far back as the early 1900s.

Downton Abbey fans will undoubtedly remember the various telegraphs that are exchanged during the show (click here for the photo source)
Morse Code has also been widely used throughout the US Military (and in other countries) for over 100 years. Some famous war movies to showcase them include The Hunt for Red October and The Imitation Game.
I recommend checking out the Morse Code Wikipedia Page and the Telegraph Wikipedia Page to learn more.
A History of Web Audio
 Web Audio Through History (click here for the source)
Web Audio Through History (click here for the source)
Now that you’ve got some background on Morse code, let’s talk about how you could use Javascript to transmit it with colors and sounds.
Sound has always been a challenge as browsers have developed. The initial web browser’s had very minimal support for sound with specific elements. When flash media was developed, it provided a cross browser solution but still required users to install software. Flash media plugins were also less than optimal.
With HTML5, the element fixed a lot of issues, but had huge limitations if you wanted to generate your own sounds from web apps. the element did not give you fine grain control over sounds and manipulation like a DJ would do.
With the advent of the Web Audio API, all of the previous challenges were resolved as it provided a framework to do (almost) any type of sound work you can think of.
Introducing the Web Audio API
I’m going to try to show a high level view of the Web Audio API in the following section. I recommend checking out the pages here for more info. You can also check out the W3C history of the Web Audio API here.
OK, so lets start at the beginning…
The Web Audio API is really just a virtual way of creating a sound system. This can be considered similar to what a DJ uses when creating “mixes”.
 (click here for the photo source)
(click here for the photo source)
The Web Audio API is really a set of “nodes” that are different parts of a virtual network. You create this network to simulate sounds and connect a source (either recorded sound or generated) to a destination (speakers). The following is a great overall diagram I copied from the MDN pages here:

The overall Audio Network that is created with the Web Audio API is called an Audio Graph. The Web Audio API calls this Audio Graph the AudioContext, which is basically where audio can run in your current browser session. Every browser has an AudioContext and you’ll need to know how to reference it to be able to use the Web Audio API.
In addition to just sound, you can also create visualizations of sound with the Web Audio API’s Analyser Node.
If all of this seems a little hard to understand, I recommend you watch the following video that walks through the basics.
Morse Sound
Now that you’ve had an introduction to Web Audio and Morse Code, let’s get to coding! In the process of learning about Morse Code, I created an app that uses the Web Audio API to generate the “dot” and “dash” sounds that you would normally hear with a telegraph or radio transmission. To create the app, I consulted the blog post here and the associated Gist here to get a better understanding of how to hook all of this up. The App is built with Angular and is hosted on Firebase.
You can play with a running version of the app here. You can also view the source code for the app on GitHub here.
Since the app follows the basic structure of Angular, I’m not going to do the standard “ng new” and app setup. I’m just going to walkthrough how the main component works with the Web APIs. Please check out the source code to see how the app was created at the GitHub link I provided above.
The app itself just takes in text, plays the text as Morse Code and also outputs the translated result as in the following screenshot.

So lets walkthrough setting this up…
First I should note that the Web Audio API is supported by most modern browsers today, but there may be small differences for specific browser implementation. The code that I’m covering here is made for Google Chrome.
As a security measure, Chrome won’t play audio without a gesture happening first. This makes sense since you don’t want apps to be able to tap into your computers audio without your consent etc. So in order to do this, the main webform of my App creates the Audio Context with the onSubmit which is tied to the main form that takes in input. Here’s the code:
onSubmit() {
if (this.audioContext === undefined) {
// Chrome requires audio context after gesture
// https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/09/autoplay-policy-changes#webaudio
this.createContext();
}
this.generateMorse(this.audioContext.currentTime, this.morseText);
}
createContext() {
this.audioContext = new AudioContext();
this.oscillator = this.audioContext.createOscillator();
this.gain = this.audioContext.createGain();
this.gain.gain.value = 0;
this.oscillator.frequency.value = 750;
this.oscillator.connect(this.gain);
this.gain.connect(this.audioContext.destination);
this.dot = 1.2 / this.rate;
this.oscillator.start(0);
}The createContext method here creates the Audio Graph that we’ve been talking about. First, we create an instance of the AudioContext, oscillator, and gain node with the following:
this.audioContext = new AudioContext();
this.oscillator = this.audioContext.createOscillator();
this.gain = this.audioContext.createGain();Next, we set the value for the gain node to be “0” to simulate it as being off (makes it not play a sound). Then we set the frequency (pitch) of the oscillator, connect the oscillator to the gain node, and connect the gain node to the speakers (audio destination) with the following:
this.gain.gain.value = 0;
this.oscillator.frequency.value = 750;
this.oscillator.connect(this.gain);
this.gain.connect(this.audioContext.destination);Finally, we set the rate at which the sounds will play and start the oscillator node. This is important because it becomes the value that we set to “schedule” sounds with the network.
this.dot = 1.2 / this.rate;
this.oscillator.start(0);The resulting Audio Graph should look somewhat like the following diagram:

In the graph here, all of the nodes exist within an AudioContext. The three Nodes that are listed here are just part of the Audio Graph. The oscillator connects to the gain which then creates output that is sent to the Speakers (Audio Destination).
With the Audio Graph setup, we next need to go about the business of creating the sounds. Here we are going to “schedule” sounds by simulating turning the gain node “on” and “off”. We do this by literally setting the gain value to “0” or “1” at specific intervals in time. Think of this like literally turning volume on and off on a speaker. We do this with the following:
generateMorse(time: any, phrase: string) {
phrase = phrase.toUpperCase();
this.morseDisplay = [];
for (const p of phrase) {
if (p === ' ') {
time += 3 _ this.dot;
} else if (this.MORSE[p] !== undefined) {
time = this.createSound(time, this.MORSE[p]);
time += 2 _ this.dot;
}
const morseOuput = new MorseOutput();
morseOuput.morseText = p;
morseOuput.morseValue = this.MORSE[p];
this.morseDisplay.push(morseOuput);
}
return time;
}The generateMorse method uses the AudioContext’s time with audioContext.currentTime property. The AudioContext has an internal clock that is continually counting once it is created. We’re going to use the audioContext.setValueAtTime method to “schedule” audio sounds using this clock. This is why the time is passed in as a parameter to the generateMorse method.
The array MORSE is just a set of key value pairs that correlate a character entered with a Morse Code value.
Also notice the use of the dot value to schedule time. This determines the frequency (pace) that the “dots” and “dashes” will be played by the program.
With the generateMorse method, the for loop walks through the phrase passed to it and then calls the createSound method. This method is where all the magic happens.
createSound(time: any, char: string) {
for (const c of char) {
switch (c) {
case '.':
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(1.0, time);
time += this.dot;
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0.0, time);
break;
case '-':
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(1.0, time);
time += 3 \* this.dot;
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0.0, time);
break;
}
time += this.dot;
}
return time;
}This method calls the gain node setValueAtTime method which “schedules” the sounds to be played within the created Audio Graph. The return value is important because it forces the Javascript Event Loop to use the sound generation as an operation on the stack. If you don’t include the return then the Javascript scope will miss the timing, and you won’t hear any sound.
Bringing it all together, the final product looks like this:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { MorseOutput } from '../models/morse-output';
@Component({
selector: 'app-morse-sound',
templateUrl: './morse-sound.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./morse-sound.component.css']
})
export class MorseSoundComponent {
private audioContext: AudioContext;
oscillator: any;
gain: any;
rate: any = 20;
dot: any;
MORSE = {
'A': '.-',
'B': '-...',
'C': '-.-.',
'D': '-..',
'E': '.',
'F': '..-.',
'G': '--.',
'H': '....',
'I': '..',
'J': '.---',
'K': '-.-',
'L': '.-..',
'M': '--',
'N': '-.',
'O': '---',
'P': '.--.',
'Q': '--.-',
'R': '.-.',
'S': '...',
'T': '-',
'U': '..-',
'V': '...-',
'W': '.--',
'X': '-..-',
'Y': '-.--',
'Z': '--..',
'1': '.----',
'2': '..---',
'3': '...--',
'4': '....-',
'5': '.....',
'6': '-....',
'7': '--...',
'8': '---..',
'9': '----.',
'0': '-----'
};
morseText = '';
morseDisplay = [];
constructor() { }
onSubmit() {
if (this.audioContext === undefined) {
// Chrome requires audio context after gesture
// https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/09/autoplay-policy-changes#webaudio
this.createContext();
}
this.generateMorse(this.audioContext.currentTime, this.morseText);
}
createContext() {
this.audioContext = new AudioContext();
this.oscillator = this.audioContext.createOscillator();
this.gain = this.audioContext.createGain();
this.gain.gain.value = 0;
this.oscillator.frequency.value = 750;
this.oscillator.connect(this.gain);
this.gain.connect(this.audioContext.destination);
this.dot = 1.2 / this.rate;
this.oscillator.start(0);
}
createSound(time: any, char: string) {
for (const c of char) {
switch (c) {
case '.':
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(1.0, time);
time += this.dot;
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0.0, time);
break;
case '-':
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(1.0, time);
time += 3 * this.dot;
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0.0, time);
break;
}
time += this.dot;
}
return time;
}
generateMorse(time: any, phrase: string) {
phrase = phrase.toUpperCase();
this.morseDisplay = [];
for (const p of phrase) {
if (p === ' ') {
time += 3 * this.dot;
} else if (this.MORSE[p] !== undefined) {
time = this.createSound(time, this.MORSE[p]);
time += 2 * this.dot;
}
const morseOuput = new MorseOutput();
morseOuput.morseText = p;
morseOuput.morseValue = this.MORSE[p];
this.morseDisplay.push(morseOuput);
}
return time;
}
}Check out the running version of the app, or do a git clone and play with the code yourself.
Morse Light
In addition to the sound App I created above, I also created a second Angular App that generates Morse Code with light. Technically, the app just uses an HTML canvas element, and redraws a circle with yellow and white to simulate a flashlight being turned on and off. Additionally, as the Morse Code light is shown, the corresponding “letter to morse” translation is output in time to the right of the light drawn.
A working version of this app is available here. You can also check out the source code on GitHub here.
Here’s a screenshot of the App in action:
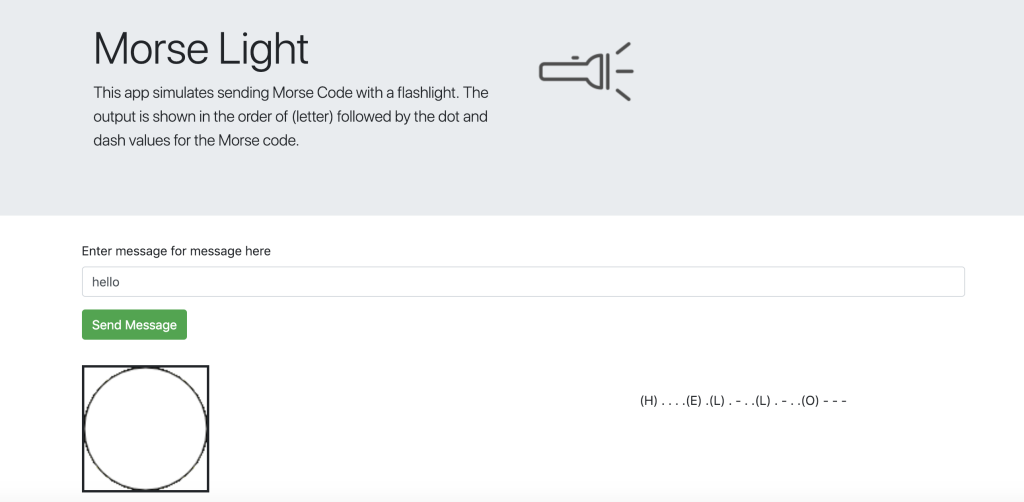
Just like with the sound App, I’m not going to go through the basics of creating the initial structure with the Angular CLI. I’m just going to focus on the main application logic here and recommend you review the project in GitHub for more on how the actual project is structured etc.
For the basic light presentation, I make use of async/await and the Javascript event loop to simulate the light being “on” and “off”. The app basically takes in a phrase as input, then makes timed calls to a method that returns a Promise. Since I’m using async/await, the main Javascript event loop is forced to wait until that Promise is resolved with the provided time. If you’re unfamiliar with async/await I recommend looking at my post here.
The app does most of the work with a transmit method and a flashlight method.
First, the transmit method is what is called by the “submit” button from the main input form. This method uses the async/await calls as I originally explained to control timing of the “on” and “off” light sequences.
async transmit() {
// time = 1200 / words per minute
// 20 words per minute
// follows a 3 to 1 ratio
// 60 milliseconds for one dot
// 180 milliseconds for a dash
// multiplied by factor of 4 to slow it down here
const dot = 60 _ 4;
const dash = 180 _ 4;
this.showMorse = '';
const messageUpper = this.message.toUpperCase();
for (const char of messageUpper) {
this.showMorse = this.showMorse + '(' + char + ') ';
const morseValue = this.morseTranslation[char];
for (const morse of morseValue) {
this.showMorse = this.showMorse + ' ' + morse;
if (morse === '.') {
// dot
await this.flashlight('yellow', dot);
// show white light to show when flash is finished
await this.flashlight('white', 60);
} else {
// dash at 3 X 60 or 180
await this.flashlight('yellow', dash);
// show white light to show when flash is finished
await this.flashlight('white', 60);
}
}
}
}As you can see in this code, the async method calls flashlight. The call has an await which blocks the main event loop, forcing the program to wait before changing the color of the light. Based on the color value that is passed in, the call to flashlight also controls the color. So yellow simulates the light being on, and white simulates the light being off. If you pass this in with a string of Morse Code in the form of dots=”.” and dashes=”-“, then you can walkthrough that line and simulate the corresponding on and off values.
flashlight(color: String, time: any): Promise<any> {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(function() {
// this.drawLight(color);
const c: any = document.getElementById('flashlight');
const ctx = c.getContext('2d');
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(c.width / 2, c.height - 50, 50, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
resolve(true);
}, time);
});
}The flashlight method just colors the canvas element for a specified amount of time. The real magic is where the async/await blocks the main thread forcing a wait before the draw/redraw of the canvas will change the lights color.
Putting it all together the Morse Light component looks like the following:
import { Component, OnInit } from "@angular/core";
@Component({
selector: "app-morse-light",
templateUrl: "./morse-light.component.html",
styleUrls: ["./morse-light.component.css"],
})
export class MorseLightComponent implements OnInit {
System: any;
message: string;
morseTranslation: any = {
A: ".-",
B: "-...",
C: "-.-.",
D: "-..",
E: ".",
F: "..-.",
G: "--.",
H: "....",
I: "..",
J: ".---",
K: "-.-",
L: ".-..",
M: "--",
N: "-.",
O: "---",
P: ".--.",
Q: "--.-",
R: ".-.",
S: "...",
T: "-",
U: "..-",
V: "...-",
W: ".--",
X: "-..-",
Y: "-.--",
Z: "--..",
"1": ".----",
"2": "..---",
"3": "...--",
"4": "....-",
"5": ".....",
"6": "-....",
"7": "--...",
"8": "---..",
"9": "----.",
"0": "-----",
" ": ".",
};
output = "";
outputLetter = "";
outputSignal = "";
showMorse = "";
constructor() {}
ngOnInit() {
const c: any = document.getElementById("flashlight");
const ctx = c.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(c.width / 2, c.height - 50, 50, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
}
async transmit() {
// time = 1200 / words per minute
// 20 words per minute
// follows a 3 to 1 ratio
// 60 milliseconds for one dot
// 180 milliseconds for a dash
// multiplied by factor of 4 to slow it down here
const dot = 60 * 4;
const dash = 180 * 4;
this.showMorse = "";
const messageUpper = this.message.toUpperCase();
for (const char of messageUpper) {
this.showMorse = this.showMorse + "(" + char + ") ";
const morseValue = this.morseTranslation[char];
for (const morse of morseValue) {
this.showMorse = this.showMorse + " " + morse;
if (morse === ".") {
// dot
await this.flashlight("yellow", dot);
// show white light to show when flash is finished
await this.flashlight("white", 60);
} else {
// dash at 3 X 60 or 180
await this.flashlight("yellow", dash);
// show white light to show when flash is finished
await this.flashlight("white", 60);
}
}
}
}
flashlight(color: String, time: any): Promise<any> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(function () {
// this.drawLight(color);
const c: any = document.getElementById("flashlight");
const ctx = c.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(c.width / 2, c.height - 50, 50, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
resolve(true);
}, time);
});
}
}Wrapping Up
Personally, all of this was a fun way to learn about Morse Code. I hope the links and Apps I created help you to understand some basics about web audio, and event timing in Javascript as well.

